Understanding Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable are an important element in fundamental analysis, a common method investors use to determine the value of a company and its securities. Because accounts receivable is a current asset, it contributes to a company’s liquidity or ability to cover short-term obligations without additional cash flows. Accounts receivable, or receivables, can be considered a line of credit extended by a company and normally have terms that require payments be made within a certain period of time. Depending on the agreement between company and client, the payment might be due in anywhere from a few days to 30 days, 60 days, 90 days, or, in some cases, up to a year.
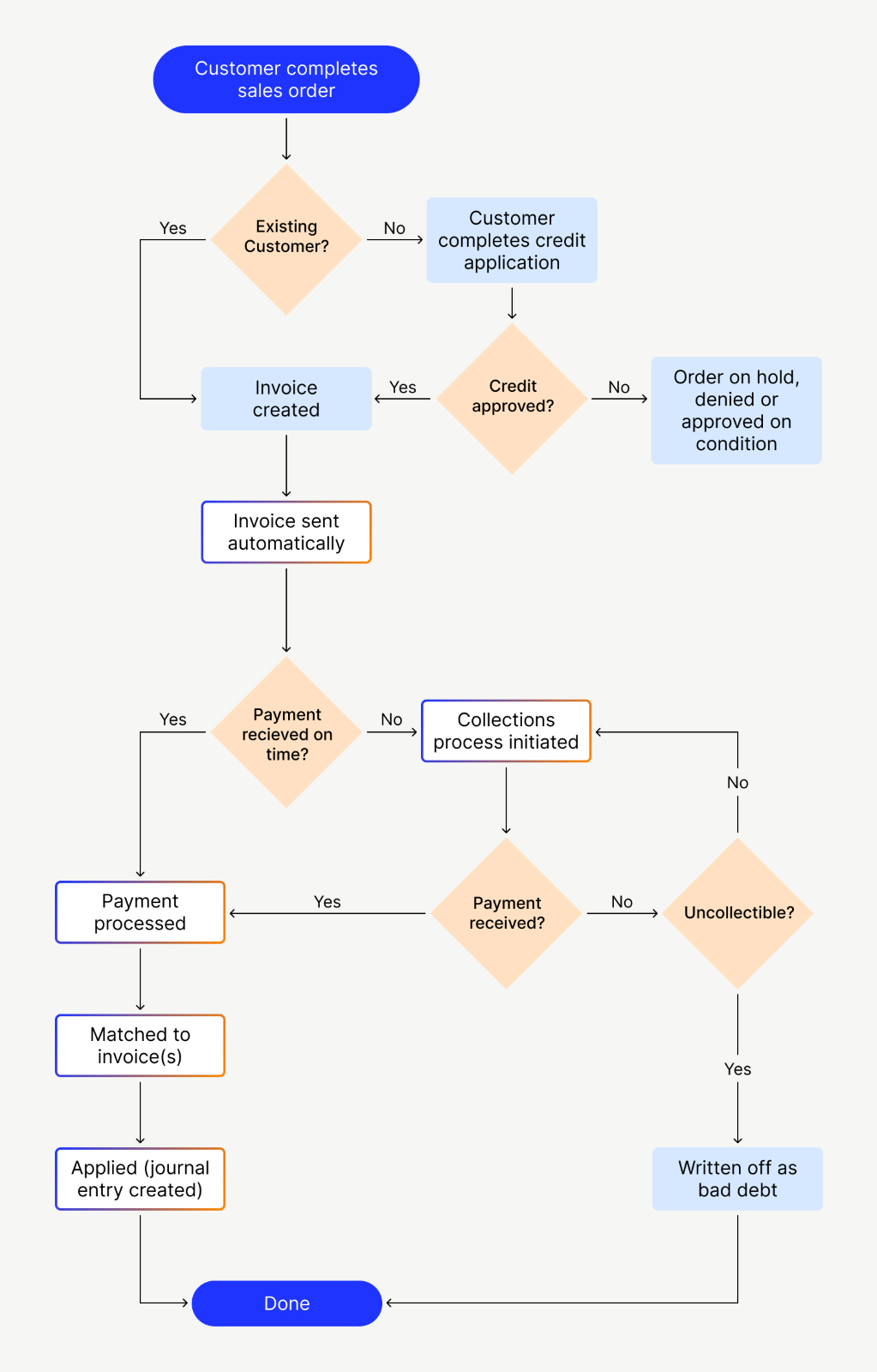
What are accounts receivable?
Once the company receives and approves this order, it generates a sales order which includes details about quantity, price, payment date, and any other relevant terms of sale. It’s an asset because it has value, and it’s a current asset because it’s expected to be collected within the next 12 months. A good accounting system with tools for managing invoice accounts receivable can help you get paid faster, so you can focus on running your business. For example, businesses that collect payments over a period of months may have a larger dollar amount of receivables in the older categories. For example, you buy $1,000 in paper from a supplier who sends you an invoice for the goods. You’d have $1,000 in accounts payable on your balance sheet for the invoice.
- The amount that the company is owed is recorded in its general ledger account entitled Accounts Receivable.
- The easiest way to handle bad debts is to use the direct write-off method.
- When the company receives cash for the credit sale on a later date, they will debit cash as it comes in and credit accounts receivable to settle the amount received in cash.
- Amortization of debt issuance costs also shall be reported as interest expense.
- Company bookkeeping may require your firm to post dozens of receivable transactions each week.
- In other words, the credit balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts tells you the amount that is to be collected from your credit customers.
Net Accounts Receivable Example
Debiting accounts receivable with $200,000 means an increase in accounts receivable by the same amount. You can use a number of strategies to increase cash collections and reduce your receivable balance. 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas.
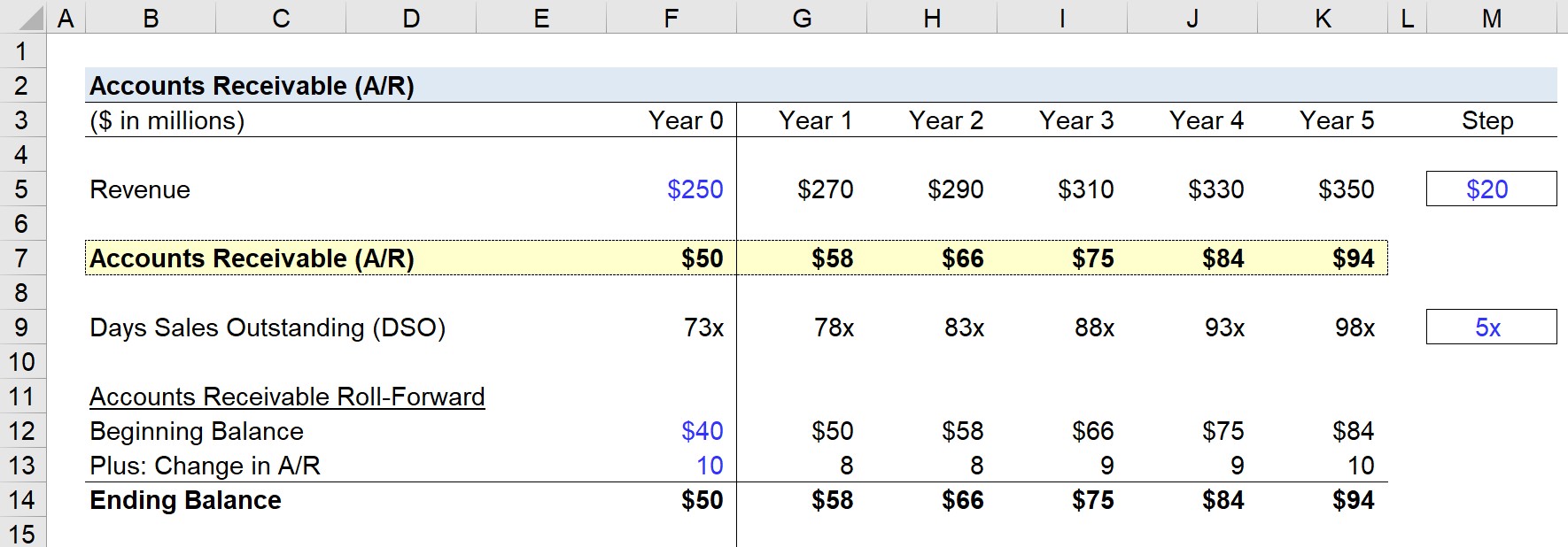
Accounts Receivable (A/R)
Some businesses will create an accounts receivable aging schedule to solve this problem. When goods or services are sold to a customer, and the customer is allowed to pay at a later date, this is known as selling on credit, and creates a liability for the customer to pay the seller. Conversely, this creates an asset for the seller, which is called accounts receivable.
Therefore, the discount or premium shall be reported in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from or addition to the face amount of the note. Similarly, debt issuance costs related to note shall be contribution margin ratio: formula definition and examples reported in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the face amount of that note. The discount, premium, or debt issuance costs shall not be classified as a deferred charge or deferred credit.
If you have to borrow from a line of credit, you’ll incur interest costs. Current asset less current liabilities equals working capital, and every business needs to generate enough in current assets to pay current liabilities. All companies should use the accrual basis of accounting to create their financial statements.
Collection agencies often take a huge cut of the collectible amount—sometimes as much as 50 percent—and are usually only worth hiring to recover large unpaid bills. Coming to some kind of agreement with the customer is almost always the less time-consuming, less expensive option. Accounts receivable are an asset account, representing money that your customers owe you. Learn how to build, read, and use financial statements for your business so you can make more informed decisions. From a practical perspective, many companies record their sale transactions as though the delivery terms were FOB shipping point, because it is easy to verify. Recording the transaction upon arrival at the customer requires substantially more work to verify.
Receivables are broadly classified into trade-receivables and non-trade receivables. Trade receivables are those receivables which originate from sales of goods and services by a business in the ordinary course of business. Non-trade receivables are the amounts due from third parties for transactions outside the primary course of business. Another way receivables may be classified is whether interest is chargeable on the amount outstanding. Colloquially, the term “accounts receivable” is also frequently used to refer to the related departments, personnel, and systems responsible for managing and tracking these unpaid debts. Net credit sales include the value of goods sold on credit for which payment is received at a later date.
You’ll lose some revenue with these payment terms, but you’ll collect some cash faster. Firms that are typically paid over a period of months will have a larger amount of receivables in the 60-day category. In any event, any contingent liability arising from discounted notes treated as sales should be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements. In the current asset section of its 31 January 2020 balance sheet, total receivables are listed net at $3,673 million.