Debits And Credits Double Entry Bookkeeping With Examples
Have a firm grasp of how debits and credits work to keep your books error-free. Accurate bookkeeping can give you a better understanding of your business’s financial health. On the other hand, a credit (CR) is an entry made on the right side of an account.
What Are Debits and Credits in Accounting?

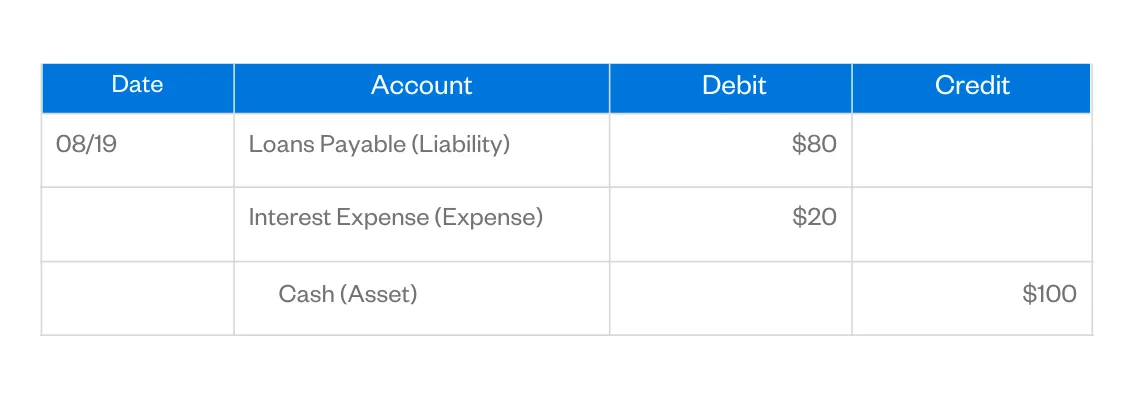
In this case, the $1,000 paid into your cash account is classed as a debit. So you’d have to record the transaction as a $1,000 debit in your cash account and a $1,000 in your bank loan account. If an adjustment is required on an account, a journal entry will be created. As with all double entries, two transactions will occur a debit and a credit.
Debits (DR)
The asset account shows the asset’s original cost and any subsequent changes in the asset’s value. A current asset representing the cost of supplies on hand at a point in time. The account is usually listed on the balance sheet after the Inventory account.
Record to Report
With the loan in place, you then debit your cash account by $1,000 to make the purchase. Angela is certified in Xero, QuickBooks, and FreeAgent accounting software. To simplify bookkeeping, she created lots of easy-to-use Excel bookkeeping templates. Accounts receivable can be managed by ensuring that invoices are sent out promptly and that payments are collected promptly.
- The three main reports are the income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows.
- For example, accumulated depreciation is a contra asset account that reduces a fixed asset account.
- Debits and credits help maintain balance in financial transactions through the double-entry bookkeeping system.
On the other hand, credits decrease asset and expense accounts while increasing liability, revenue, and equity accounts. In addition, debits are on the left side of a journal entry, and credits are on the right. A listing of the accounts available in the accounting system in which to record entries. The chart of accounts consists of balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, stockholders’ equity) and income statement accounts (revenues, expenses, gains, losses). The chart of accounts can be expanded and tailored to reflect the operations of the company. In the field of financial accounting, the term “debit” holds significant importance.
Some buckets keep track of what you owe (liabilities), and other buckets keep track of the total value of your business (equity). Recording what happens to each of these buckets using full English sentences would be tedious, so we need a shorthand. Revenue accounts track the sales of your products or services. Credits increase your equity because they show value being added to your business.
To define debits and credits, you need to understand accounting journals. A journal is a record of each accounting transaction listed in chronological order and journal entries are used by accountants for post-activity. Here are some examples of common journal entries along with their debits and credits. I’ve also added a column that shows tax definition the effect that each line of the journal entry has on the balance sheet. Debits are typically used to decrease revenue accounts, although this is rare and often related to returns or customer allowances. Conversely, a revenue account is increased by credits indicating activities that boost revenue, such as sales of products or services.
HighRadius offers a cloud-based Record to Report Suite that helps accounting professionals streamline and automate the financial close process for businesses. We have helped accounting teams from around the globe with month-end closing, reconciliations, journal entry management, intercompany accounting, and financial reporting. Review activity in the accounts that will be impacted by the transaction, and you’ll usually be able to determine which accounts should be debited and credited. Your decision to use a debit or credit entry depends on the account you are posting to, and whether the transaction increases or decreases the account. Because they are both asset accounts, your Inventory account increases with the debit while your Cash account decreases with a credit.
To credit an account means to enter an amount on the right side of an account. If you work in finance or accounting and want to save time, avoid mistakes, and impress your boss, then you have come to the right place. I’ll help automate your work and unstick your career with straightforward guides and case studies. If you don’t have enough cash to operate your business, you can use credit cards to fund operations or borrow from a line of credit.
An asset or expense account is increased with a debit entry, with some exceptions. Debits and credits are used in each journal entry, and they determine where a particular dollar amount is posted in the entry. Your bookkeeper or accountant must understand the types of accounts you use, and whether the account is increased with a debit or credit. A debit (DR) is an entry made on the left side of an account. It either increases an asset or expense account or decreases equity, liability, or revenue accounts (you’ll learn more about these accounts later). You can use Deskera to integrate directly with your business bank account, or multiple bank accounts.